Comparison and Contrast of Report Types
Capella University
ENG-FPX1250: Introduction to Technical and Business Writing
Dr.
July 20, 2023
Availability:In Stock
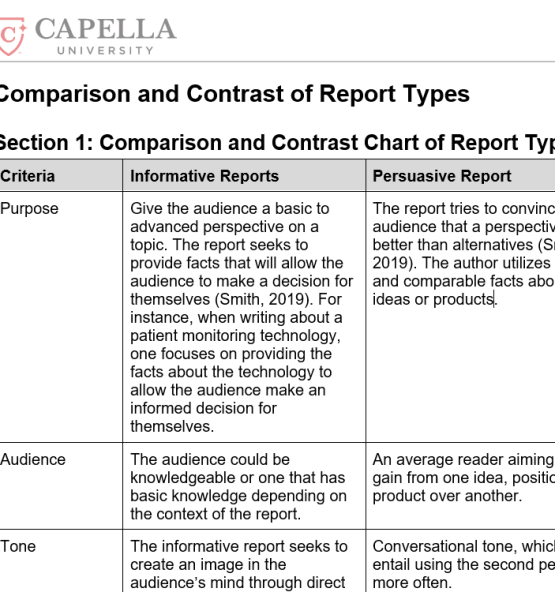
Comparison and Contrast of Report Types
Section 1: Comparison and Contrast Chart of Report Types
Criteria Informative Reports Persuasive Report
Purpose Give the audience a basic to advanced perspective on a topic. The report seeks to provide facts that will allow the audience to make a decision for themselves (Smith, 2019). For instance, when writing about a patient monitoring technology, one focuses on providing the facts about the technology to allow the audience make an informed decision for themselves. The report tries to convince the audience that a perspective is better than alternatives (Smith, 2019). The author utilizes solid and comparable facts about two ideas or products.
Audience The audience could be knowledgeable or one that has basic knowledge depending on the context of the report. An average reader aiming to gain from one idea, position, or product over another.
Tone The informative report seeks to create an image in the audience’s mind through direct and concise writing. Conversational tone, which may entail using the second person more often.
Formatting Informative reports follow a general format of an introduction, body, and conclusion (Smith, 2019). The introduction presents the topic while the body describes the facts. The conclusion wraps facts. A persuasive report has standard format. The initial paragraph is the introduction. The second, third, and fourth paragraphs provides details of the body including major arguments of the report (Smith, 2019). The last paragraph is the conclusion that summarizes arguments expressed in the report.
Style Simple, concise, and easy to read and navigate. Justifications, arguments, and reasons make the audience agree points in the report.
Writing conventions The author has to make assumptions that the audience is not as knowledgeable on the topic as they are. Correct scientific, technical terms, and labelled diagrams necessary. Sound reasoning, focus on details, and adequate consideration of alternatives.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.